Preparing your model for QuickQnect
Preparing your model for QuickQnectGeneral Considerations:
-
- All members framing into a joint must be chosen together. Partially selected extraction of a floor or area could result in a selection that leaves out members that are important to the engineering and connecting process and could lead to incorrectly connected joints. Select entire floor(s), tier(s) or even an entire building as required.
- All connecting member types must be identified in the member name, e.g.: BEAM, COLUMN, EMBED, HANGER, POST, VBRACE, HBRACE. Built up plate columns should identify the support plates as “BUILTUPCOLUMN” and built up columns with a W section and cover plates should identify the support plates as “COVERPLATE”.
- If the parameters of a member already connected are changed, for example load, beam size, etc. Qnect will provide the user the option to re-engineer the connection, explode the components, delete the components or cancel the change. However, if the user moves a member that is already connected, Qnect will only provide the user the option to explode or delete the components or cancel the change. The user must delete and re-run the connection of the moved member and any other impacting members at the new location so that Qnect will be sure to take into consideration any engineering and modelling implications of the move.
- Spandrel beams should be identified in the Qnect Specific UDA input and the shear plate (or single angle) connection must be located on the beam side towards the interior of building by choosing the proper “Near” or “Far” side beam option in the Qnect specific UDA.
- Where two or more members come to a joint, model must accurately reflect which members frame to which members. All members (including posts) in stick models must touch steel to be included in the connection detail and calculations.
- When connecting column webs, user should take into account erectability of a lower floor beam relative to upper floor. For example, if the upper floor column web has a moment connection, a lower beam may not be able to drop down and should be connected with an extended shear plate. Depending on connection preferences, this connection may need to be connected first, before connecting an entire area.
- At beams framing into roof beam (sloped less <= 1/2:12), if filler beam webs are vertical, remember to adjust as required for flange sticking through the roof line.
- If double angles are shop welded to a galvanized member, it is the detailer’s responsibility to note on shop drawing “All welds to be sealed”.
- For welds with non-low hydrogen welding process with multiple pass welds, preheating is required by the fabricator according to AWS 1.1-4.8.4
- If the material chosen in job preferences for connecting parts has a “GR.” in the nomenclature (eg. A572-GR.50) but the fabricator needs the job material defined in the drawing without “GR.” (eg. A572-50), the material name with “GR.” must be removed from the Tekla catalog in the model.
- If sequences affect part marks, sequences must be placed in model prior to connecting.
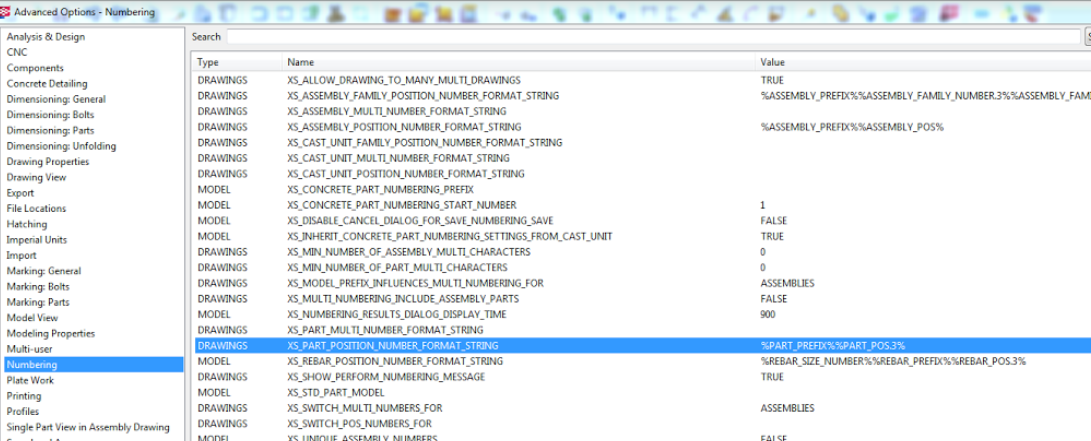
- When using part marks with 001 digits, select the requirement in Tekla “Advanced Options”.
Go to: Advance Options the select Numbering, Select: Drawings Select under name:
XS_PART_POSITION_NUMBER_FORMAT_STRING Select in value: %PART_PREFIX_%%PART_POS3%
Managing Revisions:
- When revising one member at a joint with other members, if the other members remain connected so that only individual members at the joint are selected for revision, the user must do a clash and erection check to see if the revised member connections clash with existing members or vice versa. When possible, all members at a joint should be selected together to produce the best outcome.
Design Loads:
- Reactions provided by EOR must be in the model prior to executing QuickQnect if not using UDL or force table.
- All user provided loading with LRFD design are considered to include load factors.
- If NYC Integrity, Section BC2213.2.4 is being checked, the largest compressive axial load for a column across all floors the column traverses should be entered in the column’s Tekla UDA End Condition input under compressive force.
- Fatigue Load: If Fatigue is included in the Qnect UDA, the Fatigue load will be checked only at Beam to Girder Full Depth shear plates connections with Slip Critical bolts in Standard Holes and where beam web doubler plates are not required. The check will be made according to the AASHTO LRFD 2020 Bridge Design Specifications (9th edition, 2020) based on Fatigue Load 1 for Infinite Life and the user must specify all bolt holes drilled full size or sub-punched and reamed to size. Punched holes are not allowed. (See AASHTO Table 6.6.1.2.3-1.1.5 and AASHTO Table 6.6.1.2.3-1.2.1). The detailing radius at coped beams and full depth shear plates will be set to 1 in. minimum to allow the 10 ksi stress level according to AISC 15th edition Table A-3.1-1.3.
- The column compression load needs to be included in the model at HSS columns to accurately determine HSS column yield line capacity for axially loaded shear plates. If not, Qnect will use Pr = Pc which may be conservative.
- If reactions are based on UDL, beams will be considered composite beams unless identified as non-composite from 1 of 2 methods as chosen in the Job Preferences. Option 1 – Identify beam as “NON-COMPOSITE” in Qnect Specific UDA input. Option 2 – Input “Number of Virtual Studs” in the Tekla UDA Field Studs input.
- If Shear Reaction force direction is reversed from standard gravity Shear Reaction direction (ie. filler beam web acts upwards on the connection instead of downwards), Shear Reaction force must be entered as a negative value.
- All connections to embed plates with SC bolts need the following note placed on erection drawings, “SC bolts at connections to embed plates must be pre-tensioned after concrete slab is poured”.
Moment Connections:
- Qnect will design a connection as Moment connection if “yes” is chosen to the moment connection question in the Tekla UDA End Condition input and design moment loads are provided either in the Tekla UDA End Condition input, or a plastic Moment load is defined in the Job Preferences.
Notes:
1. Moment loads should be entered as positive integers (no negative values) in the model and supersede any defined plastic moments in the Job Preferences.
2. When extended deck support plates are desired on filler beams at moment connections, please fill in Qnect UDA Deck Support checkbox at each end of beam.
3. If “yes” is chosen to the moment connection question in the Tekla UDA End Condition input, but no moment load is provided in the Tekla UDA or as a plastic Moment in the Job Preferences, the connection will not connect.
4. At connections with moment connections on both sides of the column web or flange, both beams must be selected for the proper evaluation of stiffeners and doubler requirements. Selecting one at a time is not an acceptable way to design these type of joints.
5. For moment connections to column flange, the specific compressive force in the column at the connection should be entered in the Qnect UDA to properly calculate Pr for panel zone shear capacity. If not entered, Qnect will first use the column compressive load provided in the model if provided, but if not provided in the model will calculate Pr using Pc or H1-1a per user preferences. Note: these 2 options can can cause conservative column web reinforcement or reduced connections. - Lateral Moment Connections: The Moment Load provided in the Tekla UDA End Condition input or Job Preferences plastic moment is considered Maximum Design Moment. If the user provides Gravity Load portions of Moment Load in the Qnect specific UDA input, the Lateral Moment will equal the Maximum Design Moment minus Gravity DL portion minus Gravity LL portion, and more refined combined Lateral/Gravity Moment load cases will be used for design. If Gravity Load Portions are not included in the Qnect specific UDA input, the Maximum Design Moment will be considered all Lateral Moment.
Vertical Brace Connections:
- Qnect will design a connection as Vertical Brace connection if the brace name is identified with any combination of “V” and “Brace” or “Bracing” with small or capital letters, ie. Vertical Brace, or v bracing.
- Loads for Vertical Braces can only be axial loads, and the value of the largest axial load input into the side of the brace attaching to the connection will be used for design.
- The axial load input into beams at Vertical Brace Connections is assumed to be the “Transfer Force” at the beam to column connection. If an axial force input of beams at Vertical Brace Connections is 0, or is left blank, 0 Transfer Force will be used for design in the beam to column connection.
- Brace configurations with an upper brace and lower brace will load the top brace in compression and the bottom brace in tension in order to use worst case vertical shear loading combination at beam to column connection.
- At Vertical Brace connections to column flange or web, with a Vertical Brace connection on at least one side of column and any type connections on opposite side of the column, all members on both sides of the column must be selected for the proper evaluation of design requirements. Selecting one side at a time is not an acceptable way to design these type of joints.
- Middle Beam slopes of up to 1/4 on 12 are allowed and changes to force distribution are considered negligible and not considered for design.